Note
Click here to download the full example code
Measuring hard to classify samples¶
In this example, we run an experiment on real data and try to relate the amount of hard-to-classify samples in the training set with the sampler performance.
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.metrics import pairwise_distances
from cardinal.uncertainty import MarginSampler
from cardinal.clustering import TwoStepIWKMeansSampler, TwoStepGMMSampler
from cardinal.zhdanov2019 import TwoStepKMeansSampler
from cardinal.random import RandomSampler
from cardinal.plotting import plot_confidence_interval
from cardinal.utils import ActiveLearningSplitter
np.random.seed(7)
The parameters of this experiment are:
batch_size is the number of samples that will be annotated and added to the training set at each iteration,
n_iter is the number of iterations in our simulation
We use the digits dataset and a RandomForestClassifier as model.
batch_size = 20
n_iter = 20
X, y = load_digits(return_X_y=True)
X /= 255.
n_classes = 10
model = RandomForestClassifier
Core Active Learning Experiment¶
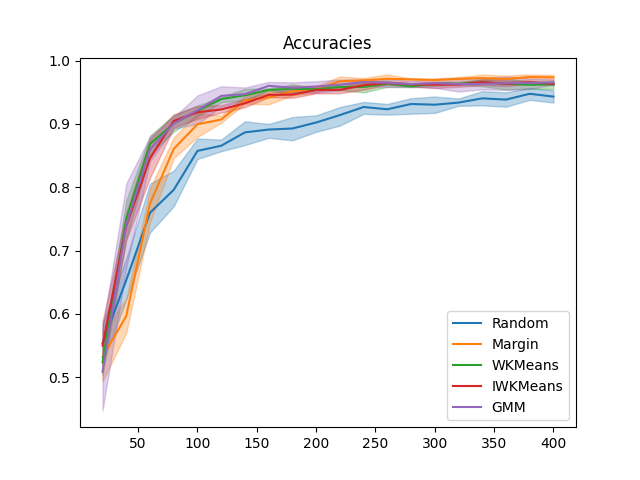
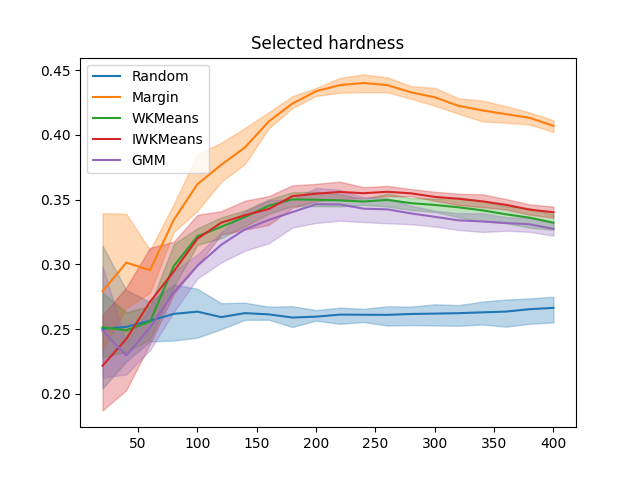
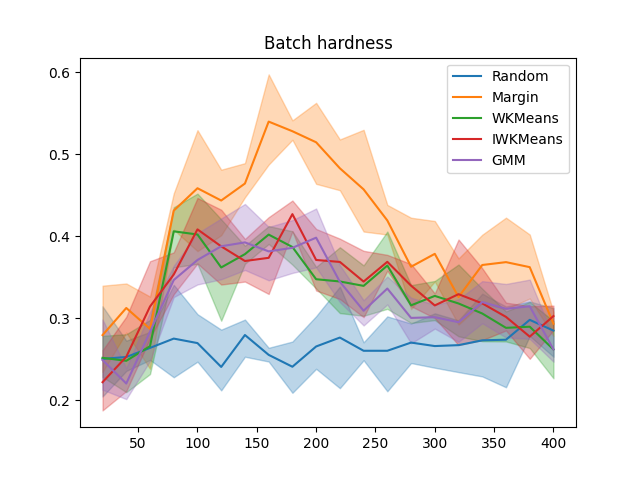
We now perform the experiment. We compare our adaptive model to random, pure exploration, and pure exploitation. We also monitor the metrics defined above.
samplers = [
('Random', lambda clf: RandomSampler(batch_size)),
('Margin', lambda clf: MarginSampler(clf, batch_size)),
('WKMeans', lambda clf: TwoStepKMeansSampler(10, clf, batch_size)),
('IWKMeans', lambda clf: TwoStepIWKMeansSampler(10, clf, batch_size)),
('GMM', lambda clf: TwoStepGMMSampler(10, clf, batch_size))
]
all_splitters = dict()
all_accuracies = dict()
all_selected_hardness = dict()
all_batch_hardness = dict()
for i, (sampler_name, sampler_gen) in enumerate(samplers):
splitters = []
all_selected_hardness[sampler_name] = []
all_batch_hardness[sampler_name] = []
all_accuracies[sampler_name] = []
for train_idx, test_idx in RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=2, n_repeats=2, random_state=i).split(X, y):
splitter = ActiveLearningSplitter(X.shape[0], test_index=test_idx)
splitter.initialize_with_random(n_classes, at_least_one_of_each_class=y[splitter.train])
X_test, y_test = X[splitter.test], y[splitter.test]
clf_trained_on_test = model().fit(X_test, y_test)
accuracies = []
batch_hardness = []
selected_hardness = []
# The classic active learning loop
for j in range(n_iter):
clf = model()
clf.fit(X[splitter.selected], y[splitter.selected])
selected_hardness.append(1. - clf_trained_on_test.predict_proba(X[splitter.selected])[np.arange(splitter.selected.sum()), y[splitter.selected]].mean())
batch_hardness.append(1. - clf_trained_on_test.predict_proba(X[splitter.batch])[np.arange(splitter.batch.sum()), y[splitter.batch]].mean())
# Record metrics
accuracies.append(clf.score(X_test, y_test))
sampler = sampler_gen(clf)
sampler.fit(X[splitter.selected], y[splitter.selected])
selected = sampler.select_samples(X[splitter.non_selected])
splitter.add_batch(selected)
all_selected_hardness[sampler_name].append(selected_hardness)
all_batch_hardness[sampler_name].append(batch_hardness)
all_accuracies[sampler_name].append(accuracies)
# Plot accuracies
plt.figure()
x_data = np.cumsum([batch_size] * n_iter)
for sampler in all_accuracies:
plot_confidence_interval(x_data, all_accuracies[sampler], label=sampler)
plt.title('Accuracies')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
x_data = np.cumsum([batch_size] * n_iter)
for sampler in all_selected_hardness:
plot_confidence_interval(x_data, all_selected_hardness[sampler], label=sampler)
plt.title('Selected hardness')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
x_data = np.cumsum([batch_size] * n_iter)
for sampler in all_batch_hardness:
plot_confidence_interval(x_data, all_batch_hardness[sampler], label=sampler)
plt.title('Batch hardness')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 3 minutes 49.765 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 32 MB