Note
Click here to download the full example code
Replay and experiment¶
In a previous example, we have shown how experiments can be resumed. Cardinal also allows for experiments to be replayed, meaning that one can save intermediate data to be able to run analysis on the experiment without having to retrain all the models. Let us now see how the ReplayCache allows it.
import shutil
import os
import numpy as np
import dataset
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from cardinal.random import RandomSampler
from cardinal.uncertainty import MarginSampler
from cardinal.cache import ReplayCache, ShelveStore, SqliteStore
from cardinal.utils import SampleSelector
Since we will be looking at the cache, we need a utility function to display a tree folder.
def print_folder_tree(startpath):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(startpath):
level = root.replace(startpath, '').count(os.sep)
indent = ' ' * 4 * (level)
print('{}{}/'.format(indent, os.path.basename(root)))
subindent = ' ' * 4 * (level + 1)
for f in files:
print('{}{}'.format(subindent, f))
We load the data and define the parameters of this experiment:
batch_sizeis the number of samples that will be annotated and added to the training set at each iteration,n_iteris the number of iterations in our simulation
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=1)
batch_size = 5
n_iter = 10
model = SVC(probability=True)
sampler = MarginSampler(model, batch_size)
experiment_config = dict(sampler='margin')
CACHE_PATH = './cache'
DATABASE_PATH = './cache.db'
value_store = ShelveStore(DATABASE_PATH)
We define our experiment in a dedicated function since we want to run it several times. We also create a dedicated exception that we will rise to simulate an interruption in the experiment.
Note the use of the SampleSelector utils that facilitate the handing of indices in an active learning experiment.
In the end, all values for all iterations are kept. The cache structure is human readable and can be shared for better reproducibility.
with ReplayCache(CACHE_PATH, value_store, keys=experiment_config) as cache:
# Create a selector with one sample from each class and persist it
init_selector = SampleSelector(X_train.shape[0])
init_selector.add_to_selected([np.where(y_train == i)[0][0] for i in np.unique(y)])
selector = cache.persisted_value('selector', init_selector)
predictions = cache.persisted_value('prediction', None)
for j, prev_selector, prev_predictions in cache.iter(range(n_iter), selector.previous(), predictions.previous()):
print('Computing iteration {}'.format(j))
model.fit(X_train[prev_selector.selected], y_train[prev_selector.selected])
sampler.fit(X_train[prev_selector.selected], y_train[prev_selector.selected])
prev_selector.add_to_selected(sampler.select_samples(X_train[prev_selector.non_selected]))
selector.set(prev_selector)
predictions.set(model.predict(X_test))
# All the values for the experiment are kept
print_folder_tree('./cache')
# This code could have been added to the script afterward to computer any metric.
def compute_contradictions(previous_prediction, current_prediction):
if previous_prediction is None:
return 0
return (previous_prediction != current_prediction).sum()
cache.compute_metric('contradictions', compute_contradictions, predictions.previous(), predictions.current())
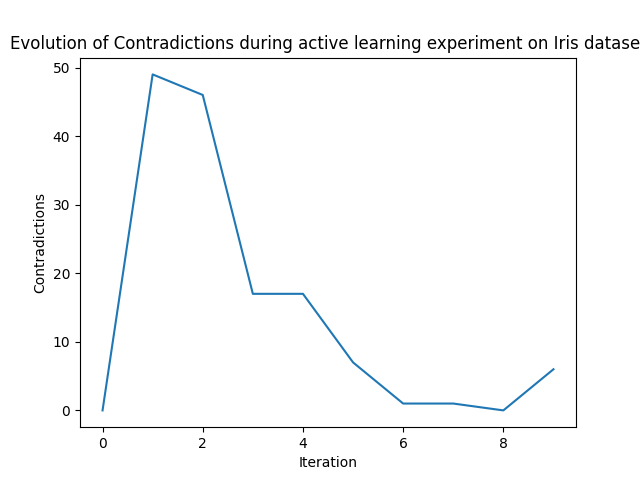
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
contradictions = value_store.get('contradictions')
plt.plot(contradictions['iteration'], contradictions['value'])
plt.xlabel('Iteration')
plt.ylabel('Contradictions')
plt.title('Evolution of Contradictions during active learning experiment on Iris dataset')
plt.show()
value_store.close()
Computing iteration 0
Computing iteration 1
Computing iteration 2
Computing iteration 3
Computing iteration 4
Computing iteration 5
Computing iteration 6
Computing iteration 7
Computing iteration 8
Computing iteration 9
cache/
sampler/
margin/
progress.json
0/
selector
prediction
1/
selector
prediction
2/
selector
prediction
3/
selector
prediction
4/
selector
prediction
5/
selector
prediction
6/
selector
prediction
7/
selector
prediction
8/
selector
prediction
9/
selector
prediction
We clean all the cache folder.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.152 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 11 MB